Liver, Pancreas & Biliary Conditions
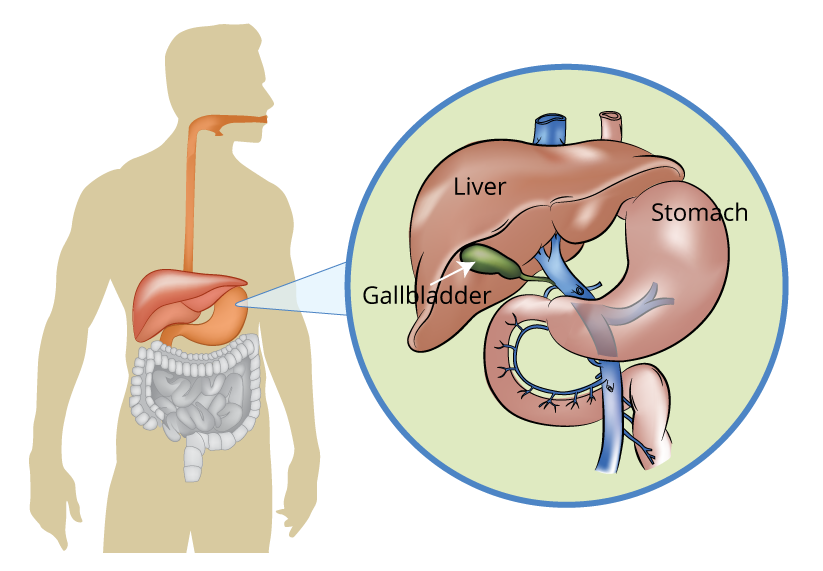
The biliary system, including the liver, pancreas and gallbladder, form a part of the body’s digestive system that is responsible for nutrient absorption and waste disposal. A number of disorders can occur in the biliary system. Some of the most common are highlighted below.
Ascites
Ascites is simply an accumulation of fluid in the abdomen that causes swelling. It most often occurs in patients with liver disease and who are in the late stages of cancer.
Symptoms
Many people do not initially notice symptoms, but as ascites become larger patients experience
- Abdominal pain or discomfort
- Bloating
- Shortness of breath
Causes
Most often, ascites are caused by
- Cirrhosis
- Severe liver disease
- Late stage cancers
Cirrhosis
Cirrhosis is a condition in which healthy liver cells are damaged over a long period of time resulting in scar tissue formation, and loss of functioning liver cells. This process eventually contributes to liver failure. Since a healthy liver is needed to survive, cirrhosis is a very serious disorder.
Symptoms
Early in the disease, people may not experience symptoms because the liver has some ability to regenerate and compensate for injury. As the disease progresses the following symptoms are common:
- fatigue or weakness
- itching
- nausea
- bloating of the abdomen from ascites—a buildup of fluid in the abdomen
- edema—swelling due to a buildup of fluid—in the feet, ankles, or legs and abdomen
- weight loss or loss of appetite
- spiderlike blood vessels on the skin or easy bruising
- jaundice, a yellowing of the skin and eyes
Causes
- Hepatitis C
- Alcohol related liver disease
- Fatty liver disease
For more information:
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/liver-disease/cirrhosis
Fatty liver disease
Fatty liver disease is simply the presence of accumulated fat in the liver. A build up of fat in the liver may cause an inflammatory process which leads to cirrhosis.
There are two main types:
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Alcoholic fatty liver disease
Symptoms
Both alcoholic and non alcoholic forms of fatty liver disease rarely cause noticeable symptoms in the early stages. When symptoms are present they may be
- fatigue or weakness
- itching
- spiderlike blood vessels on the skin or easy bruising
- jaundice, a yellowing of the skin and eyes
Causes
Alcoholic fatty liver disease is caused by heavy alcohol use and is the earliest stage of alcohol related liver disease.
Researchers unsure of the cause of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, but have found it to be more prevalent in patients who are
- Obese
- Have type 2 diabetes
- Are middle aged or older
- Have high levels of fats in the blood
For more information on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease:
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/liver-disease/nafld-nash
http://patients.gi.org/topics/fatty-liver-disease-nafld
Gallstone and Gallbladder disease
The gallbladder and its associated bile ducts form the system that carries bile to the duodenum. The pancreatic duct joins the common bile duct at the ampulla of vater in the duodenal wall. Crystallization of bile within the gallbladder or occasionally in the bile ducts results in stone formation, pain and plugging of the bile system.
Symptoms
Many patients with gallstones do not experience symptoms. However many do experience severe symptoms that include
- abdominal pain; the upper right portion or just below the breast bone are most common
- pain in upper back
- nausea or vomiting
- fever
- jaundice, a yellowing of the skin and eyes
- dark urine
- paler than usual stools
Causes
Researchers are unsure exactly why the system may become imbalanced, but have identified that certain people have a higher risk of developing gallstones or an infection of the gallbladder.
Who is at greatest risk?
- Women
- People over 40
- American Indians
- Mexican Americans
- People who are obese
- People who have experienced rapid weight loss
- Pregnant women
- Those who eat high-fat or high-cholesterol diets
- Those with diseases that affect nutrient absorption, such as Crohn’s
- Those with liver disease
For more information:
http://s3.gi.org/patients/cgp/pdf/gallstones.pdf
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/gallstones
Gilbert’s syndrome
Gilbert’s syndrome is a condition where one of the liver enzymes does not process bilirubin as efficiently. . Unconjugated bilirubin may accumulate in lager amounts causing mild intermittent jaundice. It is a common normal genetic variant that poses no health issues.
Symptoms
The main indication of Gilbert’s disease is jaundice, a yellowing of the skin and eyes
Causes
Caused by a gene mutation that controls an enzyme that breaks down bilirubin in the bloodstream.
Hemochromatosis
Hemochromatosis is a disorder in which the body simply absorbs too much iron from food. The excess accumulates in organs and joints, and can be fatal if left untreated.
Symptoms
- joint pain
- fatigue
- weight loss
- abdominal pain
- memory fog
- irregular heart beat
- loss of sex drive
Causes
Primary Hemochromatosis is an inherited genetic defect, while Secondary Hemochromatosis comes from frequent blood transfusions.
For more information:
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/liver-disease/hemochromatosis
Hepatitis
Hepatitis is an inflammation of the liver from any cause. Common causes of hepatitis include viruses, medications, toxins, and inherited liver conditions. Viral hepatitis comes from several viruses labeled A, B, C, D & E. Toxic hepatitis comes from alcohol, drugs, nutritional supplements or chemicals overloading the liver. Inherited liver problems include hemochromatosis, alpha 1 antitrypsin deficiency, and Wilson’s disease. Since a healthy liver is needed to survive hepatitis is a very serious disorder.
Symptoms
While some people do not experience symptoms, the most common are
- fatigue or weakness
- itching
- jaundice, a yellowing of the skin and eyes
- nausea or vomiting
- loss of appetite
- abdominal pain
- headache
- fever
- mental confusion
Causes
While each of the hepatitis viruses has similar symptoms, they each have different means of transmission and affect the liver differently. A laboratory test can determine which form of hepatitis is present.
Hepatitis is a complex disease. For more information see
https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis/
http://patients.gi.org/topics/viral-hepatitis/
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/liver-disease/viral-hepatitis
Jaundice
Jaundice is the term used to describe a condition where there is too much bilirubin in the blood, identified by a yellowing in the skin and eyes. It not a disease, but is a sign of underlying disorders
Symptoms
- yellowing of the skin and eyes
- fatigue or weakness
- itching
- nausea or vomiting
- loss of appetite
- abdominal pain
- fever
- dark urine
- paler than usual stools
Causes
Bilirubin is yellow-colored substance that remains in the bloodstream after iron is removed from the hemoglobin in red blood cells. If there is an obstructed bile duct or the liver is unhealthy, jaundice occurs. A number of conditions can cause this to occur.
Pancreatitis
Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas. The pancreas is a gland hidden behind the stomach. The pancreas has several functions: To produce enzymes that help digestion, to provide controlling hormones for gut function, and production of of insulin and glucagon that help control the way glucose is processed. Pancreatitis may vary from absent symptoms with elevations of amylase or lipase, to a life threatening process with severe pain and multiple systems failure.
Symptoms
- Upper abdominal pain that radiates into the back
- Swollen or tender abdomen
- Nausea or vomiting
- Fever
- Increased heart rate
Causes
- Alcoholism
- Gallstones
- Abdominal surgery
- Some medications
- High triglycerides
- Cystic fibrosis
- Some autoimmune conditions
For more information, see
http://patients.gi.org/topics/pancreatitis-acute-and-chronic/
https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/pancreatitis
Other resources:
For more information on alcoholic liver disease see http://s3.gi.org/patients/cgp/pdf/alcohol.pdf
If you are bothered by conditions of the liver, pancreas or gallbladder, our office can help. Call (706) 868-0104 for more information.
The content on our website is for informational purposes only, and is not intended to diagnose or treat any medical conditions. Always seek the advice of your physician with any questions you may have regarding your health.
